Cybersecurity risk analysis methodology
News & Insights
10 Min Read
Cybersecurity Risk Analysis Methodology: A Comprehensive Guide In today’s digital age, businesses face a constantly evolving array of cybersecurity threats. To protect assets, ensure compliance, and maintain customer trust, a structured cybersecurity risk analysis methodology is essential. This process identifies potential vulnerabilities, evaluates their impact, and provides actionable insights to mitigate risks effectively.
What is Cybersecurity Risk Analysis?
Cybersecurity risk analysis is the process of identifying, assessing, and managing risks associated with an organization’s information systems, networks, and data. It provides a clear understanding of potential threats, their likelihood, and the severity of their impact, enabling organizations to allocate resources efficiently and enhance security measures.
Key Benefits of Cybersecurity Risk Analysis
Proactive Risk Management: Identifies vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
Improved Resource Allocation: Helps prioritize investments in security tools and processes.
Regulatory Compliance: Ensures adherence to standards like GDPR, HIPAA, or ISO 27001.
Enhanced Resilience: Strengthens the organization’s ability to withstand and recover from attacks.
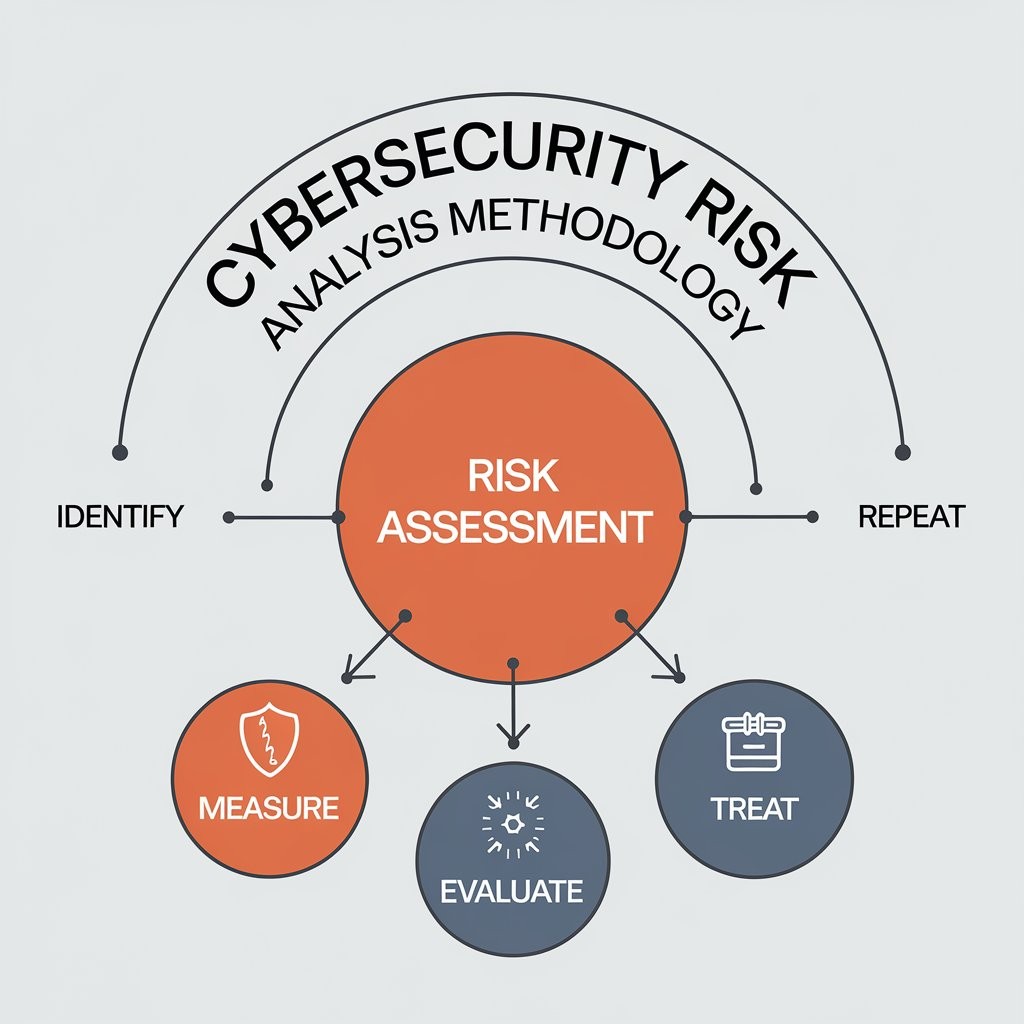
The Cybersecurity Risk Analysis Methodology
1. Define the Scope and Objectives
Before beginning the analysis, clearly define its scope. Decide which systems, data, and processes will be assessed. Identify the business objectives and regulatory requirements driving the need for the analysis.
Key Questions to Address:
What assets are critical to business operations?
Are there compliance mandates to meet?
What are the primary concerns of stakeholders?
2. Inventory and Classify Assets
Create a detailed inventory of all digital assets, including hardware, software, data, and infrastructure. Classify these assets based on their importance, sensitivity, and potential impact of a breach.
Best Practices:
Use automated tools to track assets.
Categorize data by sensitivity levels, such as public, confidential, and restricted.
3. Identify Threats and Vulnerabilities
Examine the threat landscape to identify risks relevant to your organization. These may include malware, phishing, insider threats, or system misconfigurations. Conduct a vulnerability assessment to uncover weak points.
Tools to Use:
Threat intelligence feeds (e.g., MITRE ATT&CK).
Vulnerability scanners and penetration testing tools.
4. Perform Risk Assessment
Evaluate the likelihood of identified threats exploiting vulnerabilities and assess the potential impact. Use a risk matrix to categorize risks by severity, allowing you to prioritize actions.
Risk Assessment Techniques:
Quantitative: Assign numerical values to risks for precise measurement.
Qualitative: Use categories like low, medium, and high for simplicity.
5. Develop Mitigation Strategies
Based on the risk assessment, create an action plan to address the highest-priority risks. Mitigation strategies may include implementing technical controls, revising policies, or providing employee training.
Common Mitigation Measures:
Firewalls and intrusion detection systems.
Regular software updates and patches.
Employee awareness programs.
6. Implement Security Measures
Deploy the identified mitigation strategies. Ensure seamless integration with existing systems and processes to avoid disrupting operations.
Tips for Successful Implementation:
Test new security measures in a controlled environment.
Provide training for IT teams and employees.
7. Monitor and Review Regularly
Cybersecurity is not a one-time effort. Continuously monitor your systems and processes for emerging threats and vulnerabilities. Periodically review the risk analysis to adapt to new challenges.
Monitoring Tools:
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) solutions.
Real-time vulnerability scanning tools.
Common Challenges in Cybersecurity Risk Analysis
Dynamic Threat Landscape: Threats evolve rapidly, requiring constant vigilance.
Resource Constraints: Limited budgets and personnel can hinder analysis efforts.
Complexity of IT Environments: Diverse systems and devices add layers of difficulty.
Data Accuracy: Outdated or incomplete data can skew the analysis.
Best Practices for Effective Cybersecurity Risk Analysis
Adopt Established Frameworks: Use standards like NIST RMF, ISO 27005, or FAIR for a structured approach.
Leverage Automation: Utilize tools to streamline asset tracking, threat detection, and reporting.
Engage Stakeholders: Involve key personnel across departments to align security goals with business objectives.
Regularly Update Policies: Ensure that security policies evolve with the threat landscape.
Join our newsletter list
Sign up to get the most recent blog articles in your email every week.