Cybersecurity risk management for non-profits
News & Insights
6 Min Read
Protecting Your Mission: Cybersecurity Risk Management for Non-Profits Non-profit organizations are dedicated to making a positive impact on the world, but this dedication often comes with a unique set of cybersecurity challenges. Non-profits handle sensitive data, from donor information to beneficiary records, making them attractive targets for cybercriminals. A robust cybersecurity risk management plan is essential for protecting your mission, your data, and your stakeholders.
Why Cybersecurity is Critical for Non-Profits
Non-profits face a distinct set of challenges when it comes to cybersecurity:
Limited Resources: Many non-profits operate with tight budgets and limited staff, making it difficult to invest in comprehensive cybersecurity solutions.
Volunteers and Staff Turnover: High turnover rates can create vulnerabilities if staff aren't adequately trained in cybersecurity best practices.
Reliance on Donors: Data breaches and security incidents can damage an organization's reputation and impact donor trust.
Public Trust: Non-profits often operate with a high level of public trust, making them attractive targets for those seeking to exploit organizations for financial gain.
Sensitive Data: Non-profits often handle sensitive information, such as donor financial data and beneficiary personal information, requiring a high level of security.
Vulnerability to Scams: Non-profits are often targeted by phishing, business email compromise (BEC), and other scams, often resulting in financial loss.
What is Cybersecurity Risk Management?
Cybersecurity risk management is the process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating cybersecurity risks to protect your organization's assets and operations. It involves a systematic approach that helps you understand your vulnerabilities and prioritize security measures. This process should be ongoing, adaptable to evolving threats, and integrated with the organization’s strategic planning.
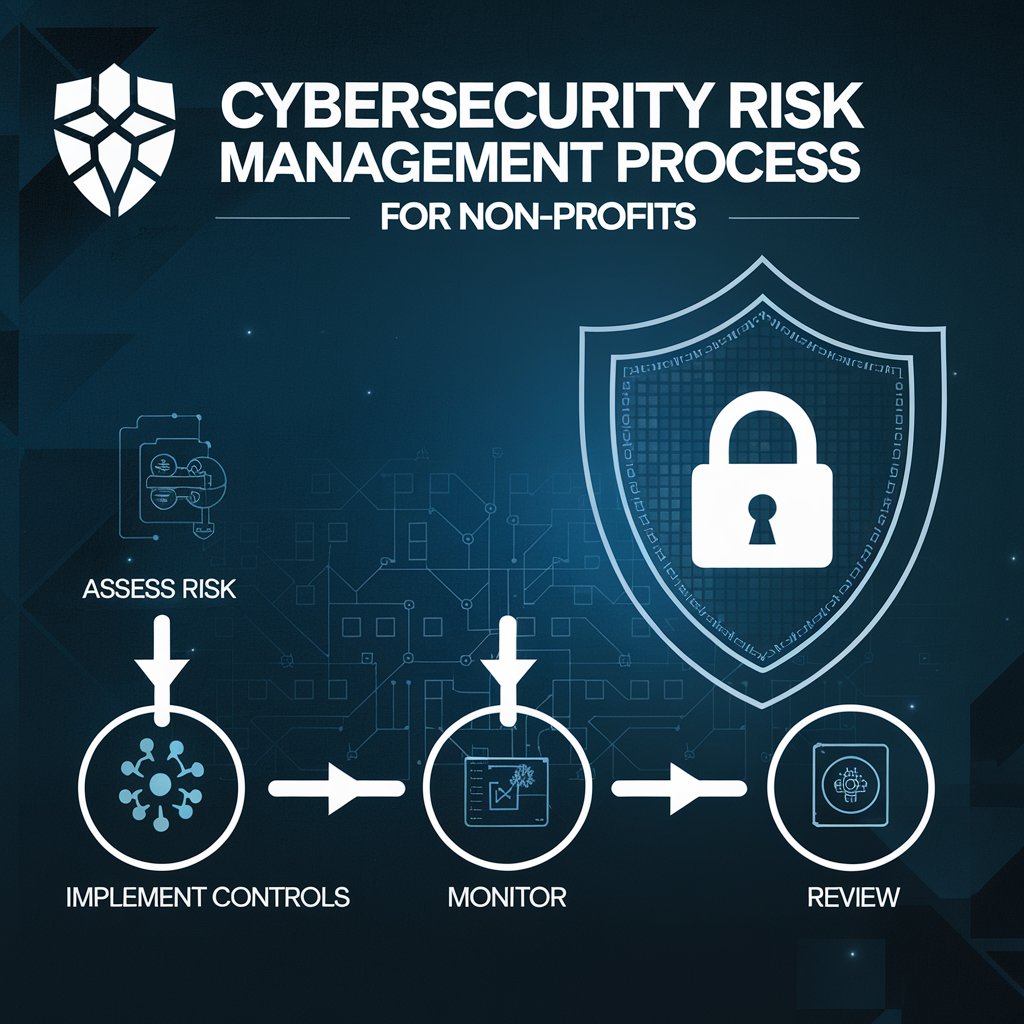
Key Steps in Cybersecurity Risk Management for Non-Profits
Here's a breakdown of the essential steps for non-profits to manage cybersecurity risks effectively:
Identify Your Assets:
What it is: Create an inventory of all digital assets, including hardware, software, data, and network devices.
Why it matters: Knowing what you need to protect is the foundation of any security plan.
Examples: Computers, servers, websites, databases, donor lists, financial records, volunteer information, and social media accounts.
Identify Potential Threats:
What it is: Identify the potential threats your organization might face.
Why it matters: Understanding the threat landscape helps you focus your security efforts.
Examples: Malware, ransomware, phishing attacks, data breaches, denial-of-service attacks, insider threats, and physical theft.
Assess Your Vulnerabilities:
What it is: Analyze your systems and identify potential weaknesses that could be exploited.
Why it matters: Vulnerabilities are the pathways attackers use to compromise your organization.
Examples: Outdated software, weak passwords, lack of encryption, misconfigured firewalls, and a lack of user training.
Evaluate Risk:
What it is: Determine the likelihood and potential impact of each identified risk.
Why it matters: Helps you prioritize security measures based on the most significant threats.
Risk Matrix: Use a risk matrix (likelihood vs. impact) to categorize and prioritize risks.
Develop a Cybersecurity Plan:
What it is: Create a comprehensive plan that outlines your security policies, procedures, and controls.
Why it matters: Provides a roadmap for implementing and maintaining your cybersecurity measures.
Elements: Include access control, data protection, incident response, employee training, and business continuity.
Implement Security Controls:
What it is: Put security controls in place to mitigate the identified risks.
Why it matters: Controls are the tools and procedures you use to protect your assets.
Examples: Firewalls, antivirus software, multi-factor authentication (MFA), data encryption, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and security awareness training.
Monitor and Review:
What it is: Continuously monitor your security controls and regularly review your risk management plan.
Why it matters: Ensures that your security measures remain effective and adapt to new threats.
Steps: Regularly update policies, conduct vulnerability scans, and test incident response plans.
Train Your Staff and Volunteers:
What it is: Provide ongoing cybersecurity training to all employees and volunteers.
Why it matters: Human error is a major cause of security breaches.
Topics: Cover phishing, password security, safe internet practices, and reporting security incidents.
Cost-Effective Cybersecurity Measures for Non-Profits
Given budgetary limitations, non-profits should focus on cost-effective cybersecurity measures:
Strong Passwords and MFA: Enforce strong passwords and enable MFA for all accounts.
Regular Software Updates: Keep all software and systems updated with the latest security patches.
Free Security Tools: Leverage free security tools like antivirus software and firewalls.
Phishing Awareness Training: Regularly educate staff on identifying phishing scams.
Data Backups: Implement regular data backups and test restoration procedures.
Security Policies and Procedures: Develop and implement clear security policies and procedures.
Utilize Cloud Security: Leverage the security features offered by cloud service providers, but ensure proper configurations.
Seeking Expert Help
If your non-profit lacks in-house expertise, consider these options:
Volunteer IT Professionals: Recruit volunteer IT professionals or partner with local tech groups.
Pro Bono Cybersecurity Services: Some cybersecurity firms offer pro bono services to non-profits.
Managed Security Services: Consider using a managed security service provider for ongoing security monitoring and management.
Conclusion:
Cybersecurity risk management is not optional; it's a necessity for non-profits. By proactively addressing security risks, non-profits can safeguard their valuable data, protect their reputation, and ensure that they can continue to focus on their mission. With limited resources, you can still implement cost-effective strategies to protect your organization. A little planning and training can go a long way in securing your non-profit organization.
Call to Action:
What cybersecurity challenges does your non-profit face?
What security measures have you found effective?
Share your experiences and ask questions in the comments below!
Key takeaways from this blog post:
Non-Profit Focus: Specifically addresses the unique cybersecurity challenges of non-profit organizations.
Clear Risk Management Process: Provides a clear and actionable risk management process.
Practical Advice: Offers cost-effective strategies and actionable tips.
Resource Suggestions: Suggests ways to seek help for limited resources.
Non-Technical Language: Uses easy-to-understand language.
Engaging Call to Action: Encourages reader participation and questions. audit3aa
Join our newsletter list
Sign up to get the most recent blog articles in your email every week.