How to conduct a cybersecurity risk assessment
News & Insights
5 Min Read
Identifying Your Weak Spots: A Practical Guide to Conducting a Cybersecurity Risk Assessment In today's threat-filled digital world, knowing where your vulnerabilities lie is the first step towards protecting your organization. A cybersecurity risk assessment is a critical process that helps you identify, analyze, and prioritize potential security risks. It's like a health checkup for your business, highlighting areas that need attention to prevent costly breaches and business disruptions.
This post will guide you through the essential steps of conducting a cybersecurity risk assessment, empowering you to strengthen your security posture and protect your valuable assets.
Why Conduct a Cybersecurity Risk Assessment?
Before diving into the "how," let's understand the "why." A risk assessment offers numerous benefits:
Identifies Vulnerabilities: Uncovers weaknesses in your systems, applications, and processes that could be exploited by attackers.
Prioritizes Risks: Helps you focus on the most critical risks that could have the biggest impact on your business.
Guides Security Investments: Provides a basis for making informed decisions about security investments and resource allocation.
Improves Security Posture: Enables you to implement appropriate security controls and mitigate potential threats.
Ensures Compliance: Helps you meet regulatory requirements and industry standards for data protection.
Reduces Financial Losses: Prevents costly data breaches, reputational damage, and business disruption.
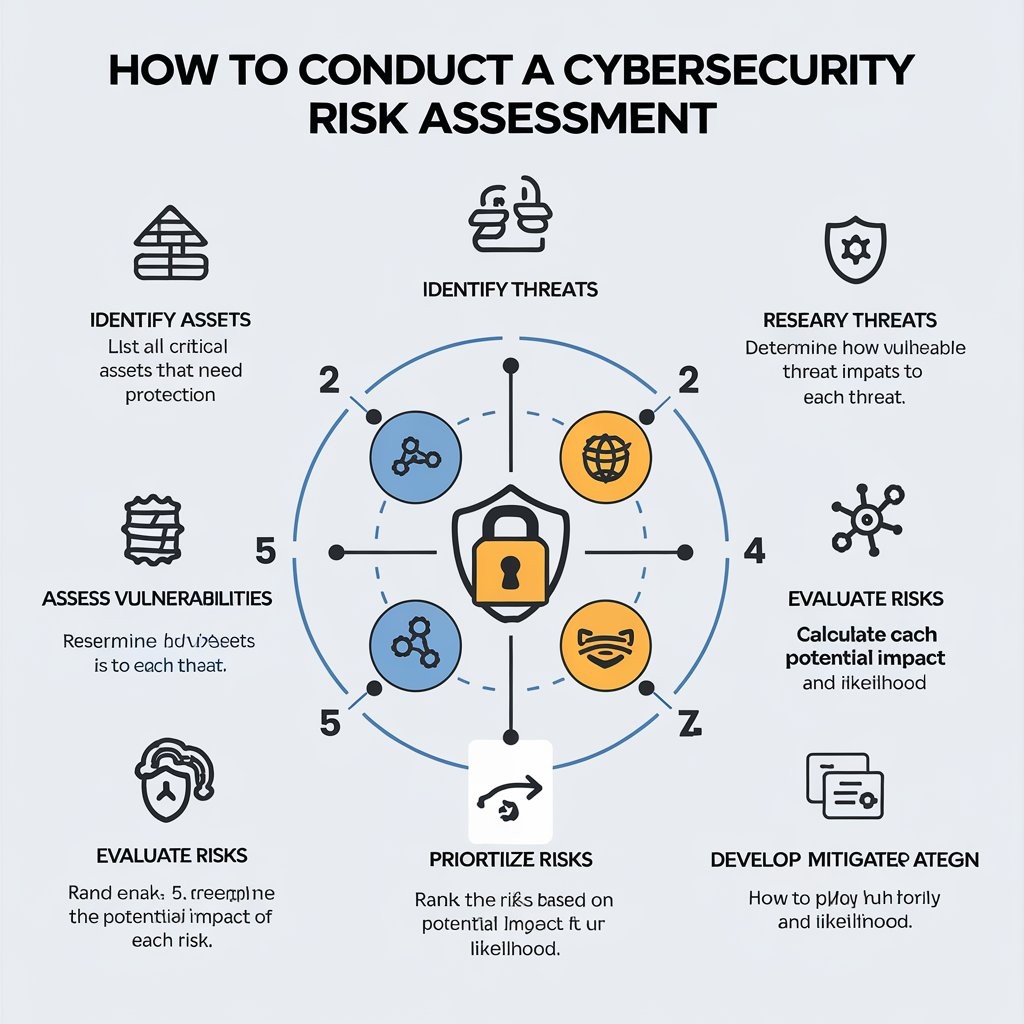
Step-by-Step Guide to Conducting a Cybersecurity Risk Assessment
Here's a practical, step-by-step approach to conducting a cybersecurity risk assessment:
Define Scope and Objectives:
Scope: Determine the boundaries of your assessment (e.g., specific systems, departments, or locations).
Objectives: Define the specific goals you want to achieve with the assessment (e.g., identify vulnerabilities, prioritize risks, improve compliance).
Stakeholders: Identify key stakeholders who should be involved in the process.
Identify Assets:
Information Assets: Identify and categorize your sensitive data, including customer data, financial records, and intellectual property.
Hardware Assets: Identify your servers, computers, mobile devices, network equipment, and other hardware.
Software Assets: Identify your operating systems, applications, and other software.
Physical Assets: Identify physical locations, such as offices, data centers, and server rooms.
Identify Threats:
External Threats: Identify potential threats from external sources, such as hackers, malware, and denial-of-service attacks.
Internal Threats: Identify potential threats from within your organization, such as accidental data leaks, malicious employees, or human error.
Common Threats: Consider common threats like phishing attacks, ransomware, and social engineering.
Identify Vulnerabilities:
Software Vulnerabilities: Identify weaknesses in your operating systems, applications, and other software.
Network Vulnerabilities: Identify vulnerabilities in your network infrastructure, such as weak firewalls or insecure configurations.
Hardware Vulnerabilities: Identify vulnerabilities in your hardware, such as outdated equipment or insecure configurations.
Human Vulnerabilities: Identify weaknesses in human behavior, such as poor password practices or lack of security awareness.
Analyze Potential Impacts:
Financial Impact: Estimate the potential financial loss from a security breach (e.g., costs of recovery, fines, and lost revenue).
Operational Impact: Estimate the potential disruption to business operations (e.g., downtime, loss of productivity).
Reputational Impact: Estimate the potential damage to your brand image and customer trust.
Legal and Regulatory Impact: Consider the potential legal and regulatory consequences of a data breach.
Data Impact: Assess the potential impact of data loss, theft, or corruption.
Assess Risk Likelihood:
Historical Data: Consider any historical data related to security incidents.
Vulnerability Data: Assess the likelihood of a threat exploiting identified vulnerabilities.
Threat Intelligence: Use threat intelligence to assess the likelihood of specific threats.
Calculate Risk Level:
Risk = Likelihood x Impact: Use a risk matrix to combine the likelihood and impact of each identified risk.
Risk Levels: Categorize risks into levels, such as low, medium, and high.
Prioritize Risks:
Focus on High Risks: Prioritize the risks that have the highest likelihood and impact.
Resource Allocation: Focus resources on mitigating the most critical risks first.
Develop Mitigation Strategies:
Risk Avoidance: Eliminate the risk altogether (e.g., stop using a vulnerable system).
Risk Reduction: Implement security controls to reduce the likelihood or impact of the risk.
Risk Transfer: Transfer the risk to a third party (e.g., purchase cyber insurance).
Risk Acceptance: Accept the risk if the cost of mitigation is too high.
Document and Communicate Results:
Report: Document your findings and recommendations in a comprehensive report.
Communicate: Share your findings with relevant stakeholders, including management and IT staff.
Monitor and Review:
Regularly Assess: Conduct regular risk assessments to monitor your security posture and adapt to changing threats.
Update Controls: Update security controls as needed to address new risks. audit3aa
Join our newsletter list
Sign up to get the most recent blog articles in your email every week.