Risk management frameworks for cybersecurity
Tutorials & Tips
10 Min Read
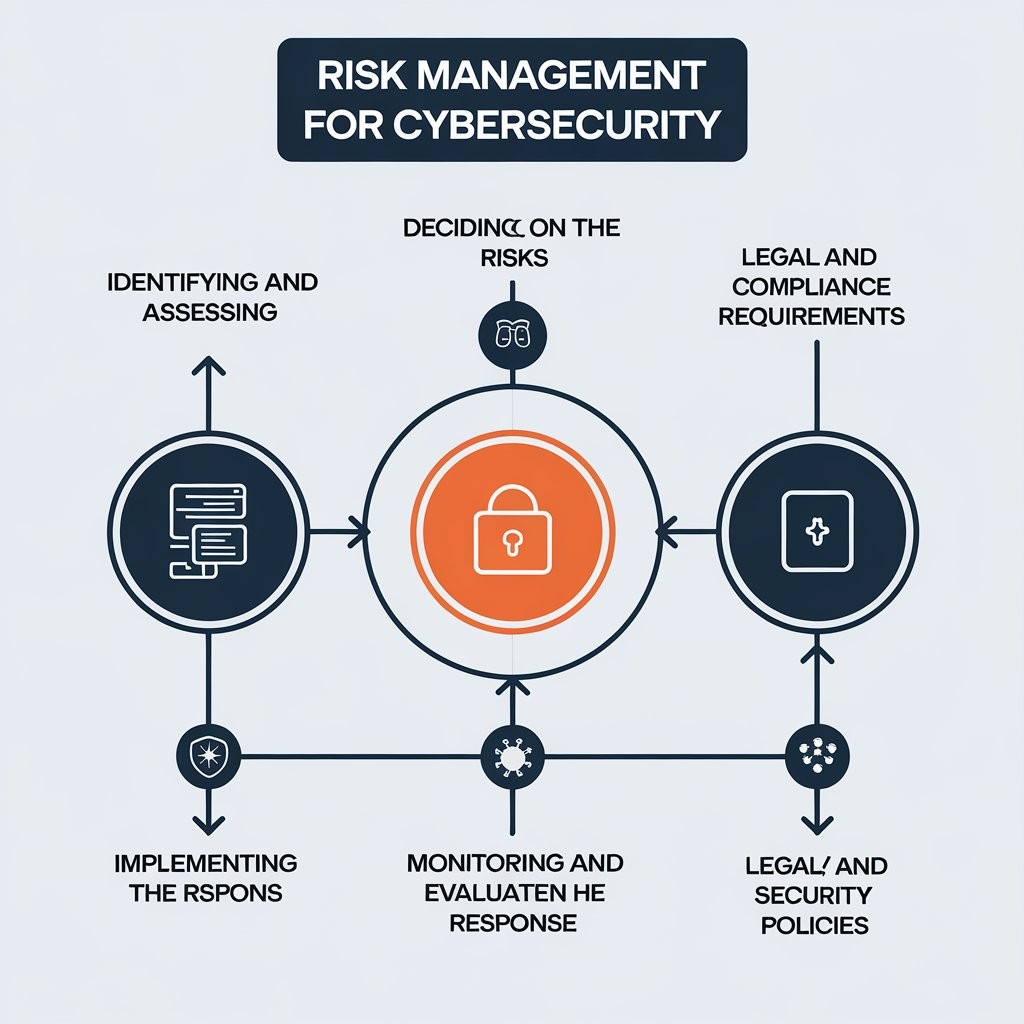
Risk Management Frameworks for Cybersecurity Risk management is crucial for any organization looking to protect its digital assets, data, and infrastructure from cybersecurity threats. A well-structured cybersecurity risk management framework provides a systematic approach to identifying, assessing, mitigating, and monitoring cybersecurity risks. These frameworks guide organizations in developing security strategies that align with business goals, legal requirements, and industry standards. In this post, we’ll explore the most widely used cybersecurity risk management frameworks that organizations can implement to improve their security posture and ensure a proactive defense against cyber threats.
1. NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF)
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cybersecurity Framework is one of the most widely adopted frameworks for managing cybersecurity risk. It was developed to help organizations across various sectors address cybersecurity challenges in a structured manner.
Core Functions:
Identify: Understand the organization's cybersecurity risks, assets, and resources.
Protect: Implement measures to safeguard assets and data, including access control and encryption.
Detect: Establish continuous monitoring and detection processes for identifying cybersecurity incidents.
Respond: Develop response strategies for cybersecurity events, ensuring timely mitigation of threats.
Recover: Enable swift recovery from cybersecurity incidents, minimizing downtime and data loss.
Why It’s Important:
NIST CSF is flexible, allowing organizations of all sizes and industries to adopt and tailor it according to their needs. It is particularly beneficial for aligning cybersecurity practices with business objectives.
2. ISO/IEC 27001
The ISO/IEC 27001 standard is part of the ISO/IEC 27000 series and focuses on information security management systems (ISMS). It provides a comprehensive framework for managing sensitive company information and ensuring its confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
Key Components:
Context of the Organization: Define the internal and external issues that affect cybersecurity risk management.
Leadership Commitment: Ensure top management support for the ISMS and risk management initiatives.
Risk Assessment and Treatment: Identify and assess cybersecurity risks, then implement risk treatment plans to manage them.
Continuous Improvement: Implement a continual improvement process for managing risks and addressing emerging threats.
Why It’s Important:
ISO/IEC 27001 is globally recognized and provides a structured approach to managing information security risks. Its focus on risk management and continuous improvement makes it a solid choice for organizations aiming to strengthen their security posture.
3. NIST SP 800-53 (Security and Privacy Controls)
The NIST Special Publication 800-53 provides a comprehensive catalog of security controls for federal information systems and organizations. Although initially designed for the U.S. federal government, it has been widely adopted by private-sector organizations for cybersecurity risk management.
Key Features:
Security Controls: Provides a comprehensive set of security and privacy controls that organizations can implement based on risk assessment.
Risk Assessment: Guides organizations through identifying potential risks and threats, assessing their impact, and applying controls to mitigate them.
System and Communications Protection: Ensures the integrity and confidentiality of information through access control and encryption measures.
Why It’s Important:
NIST SP 800-53 helps organizations implement detailed, risk-based security controls. Its flexibility allows it to be used by organizations of different sizes and sectors.
4. COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies)
COBIT is a risk management framework that focuses on IT governance and management. It provides a set of best practices for IT management and governance to help organizations align their IT and cybersecurity strategies with business goals.
Key Components:
Governance and Management Objectives: COBIT outlines 40 governance and management objectives to support cybersecurity initiatives.
Risk Management: It incorporates a strong risk management component that ensures proper assessment and mitigation of risks.
Performance Management: COBIT includes performance measures to ensure cybersecurity initiatives are achieving desired outcomes.
Why It’s Important:
COBIT is especially useful for aligning IT processes with business objectives, ensuring that cybersecurity and IT governance work together to mitigate risks and improve security.
5. CIS Controls (Center for Internet Security)
The CIS Controls are a set of 18 prioritized cybersecurity best practices designed to help organizations protect themselves from common cyber threats. The framework focuses on actionable, low-cost, and high-impact security controls.
Key Components:
Basic Controls: The first five controls focus on fundamental areas like inventory management, patch management, and controlled use of administrative privileges.
Foundational Controls: The next ten controls focus on implementing advanced technical measures such as email and web browser protections.
Organizational Controls: The final three controls emphasize security management and incident response processes.
Why It’s Important:
CIS Controls are practical and provide a clear roadmap for improving an organization’s cybersecurity posture. They are especially beneficial for small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) that lack dedicated security teams.
6. FAIR (Factor Analysis of Information Risk)
FAIR is a quantitative risk management framework that helps organizations assess the financial impact of cybersecurity risks. It provides a structured approach to evaluate risk in terms of potential loss and its probability.
Key Features:
Risk Quantification: FAIR emphasizes the importance of quantifying risk and its impact on business operations and financial performance.
Risk Analysis: Helps organizations prioritize cybersecurity risks based on their potential business impact, allowing for more effective decision-making.
Financial Decision Making: FAIR enables organizations to align cybersecurity risk management with financial goals, ensuring that resources are allocated effectively.
Why It’s Important:
FAIR allows organizations to make data-driven decisions about cybersecurity investments and risk mitigation strategies. It is especially useful for organizations that need to prioritize cybersecurity risks based on financial or business consequences.
7. OCTAVE (Operationally Critical Threat, Asset, and Vulnerability Evaluation)
OCTAVE is a risk management framework developed by Carnegie Mellon University that focuses on identifying and managing risks associated with critical assets and operations.
Key Components:
Asset Identification: Identifying key assets (data, processes, systems) that are critical to business operations.
Risk Assessment: Evaluating vulnerabilities and potential threats that could impact the identified assets.
Risk Mitigation: Developing strategies to reduce the identified risks, including technical, procedural, and organizational measures.
Why It’s Important:
OCTAVE is particularly effective for organizations that want to focus on managing risks related to their most critical business operations and data. It’s a great framework for those looking for a practical, asset-based approach to cybersecurity risk management.
8. ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library)
ITIL is a set of practices for IT service management (ITSM) that focuses on aligning IT services with business needs. While not exclusively a cybersecurity framework, ITIL’s principles can be applied to cybersecurity risk management to improve IT governance and service reliability.
Key Components:
Service Strategy: Develop a strategy that aligns IT services with business goals, including cybersecurity goals.
Service Design: Design security services that meet business needs and comply with industry standards.
Service Operation: Ensure that cybersecurity operations are executed smoothly to protect the IT infrastructure.
Why It’s Important:
ITIL helps organizations optimize their IT service delivery, ensuring that cybersecurity operations are integrated into broader business strategies and objectives. audit3aa
Join our newsletter list
Sign up to get the most recent blog articles in your email every week.